A flange is used to join pipe, valves, or a vessel within a system.The simple concept of a flange,as we noted before that a Flange with Class 400 can handle more pressure than a Class 150 flange, because a Class 400 flange are constructed with more metal and will endure more pressure. However, there are a number of factors that can impact the pressure capability of a flange.
The Pressure Class or Rating for flanges will be given in pounds. Different names are used to indicate a Pressure Class. It means that 3000 Lb or 300 Lbs or 300# or Class 300 are all the same.
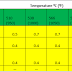
Pressure-temperature ratings are maximum allowable working gage pressures in bar units at the temperatures in degrees Celsius. As temperature increases, the pressure rating of the flange decreases. When the pressure goes down, the temperature goes up. As Example a class 300 flange of group 2.1 material at 50 degree Celsius rated at 47.8 bar pressure, 34.5 bar at 200 degree Celsius, 30.9 bar at 300 degree Celsius. At the same group material, for intermediate temperatures linear interpolation is permitted but interpolation between class designations is not permitted. Standard that governing pipe flanges and flanged fitting is ASME B16.5 .
Weldneck Flange
is normally used for high-pressure, cold or hot temperatures.
Slip On Flanges
The Pressure Class or Rating for flanges will be given in pounds. Different names are used to indicate a Pressure Class. It means that 3000 Lb or 300 Lbs or 300# or Class 300 are all the same.
Pressure-temperature ratings are maximum allowable working gage pressures in bar units at the temperatures in degrees Celsius. As temperature increases, the pressure rating of the flange decreases. When the pressure goes down, the temperature goes up. As Example a class 300 flange of group 2.1 material at 50 degree Celsius rated at 47.8 bar pressure, 34.5 bar at 200 degree Celsius, 30.9 bar at 300 degree Celsius. At the same group material, for intermediate temperatures linear interpolation is permitted but interpolation between class designations is not permitted. Standard that governing pipe flanges and flanged fitting is ASME B16.5 .
 |
| Pressure Temperature Rating for Group 2.1 Material |
Flanges Type
The most common flange types according to ASME B16.5 are: Welding Neck, Slip On and Lap Joint, Socket Weld, , Threaded and Blind flange. Short description for each type can be found below.Weldneck Flange
is normally used for high-pressure, cold or hot temperatures.
 |
| Weldneck Flange (Source :http://www.proflange.com/) |
Slip On Flanges
A slip-on flange is bored slightly larger than the OD of the matching pipe. The pipe slips into the flange prior to welding both inside and outside to prevent leaks.
Threaded Flange
 |
| 1. slip on flange 2. filled weld outside 3. filled weld inside 4. pipe (Source : http://_www.steelfittings-flange.com/) |
Is used in systems not involving temperature or stresses of any magnitude. The advantages of this yipe is that it can be attached to the pipe without welding. This type of flanges is not suitable for a pipe with thin wall thickness.
 |
| 1. Threaded flange 2. Thread 3. Pipe or Fitting (Source : http://_www.steelfittings-flange.com/) |
Socket Weld Flange
This flange is similar to slip-on flange, except they
have a bore and a counter bore. The purpose for the bottoming clearance in a socket weld is usually to reduce the residual stress at the root of the weld that could occur during solidification of the weld metal.
The counter bore is slightly larger than the OD of the matching pipe, allowing the pipe to be inserted. A restriction is built into the bottom of the bore, which acts as a
shoulder for the pipe to rest on, and has the same ID of the matching pipe. The flow is not restricted in any direction.
The counter bore is slightly larger than the OD of the matching pipe, allowing the pipe to be inserted. A restriction is built into the bottom of the bore, which acts as a
shoulder for the pipe to rest on, and has the same ID of the matching pipe. The flow is not restricted in any direction.
The disadvantage of this flange is right the gap, that must be made. By corrosive products, and mainly in stainless steel pipe systems, the crack between pipe and flange can give corrosion problems.
 |
| 1. socket weld flange 2. filled weld 3. pipe X=expansion gap (Source : http://_www.steelfittings-flange.com/) |
Blind Flange
Blind Flange has no bore, and is used to close ends of piping systems. A blind flange also permits easy access to a line once it has been sealed. The blind flange is sometimes machined to accept a pipe of the nominal size to which the reduction is being made.The reduction can be either threaded or welded.
Blind Flange has no bore, and is used to close ends of piping systems. A blind flange also permits easy access to a line once it has been sealed. The blind flange is sometimes machined to accept a pipe of the nominal size to which the reduction is being made.The reduction can be either threaded or welded.
 |
| 1. Blind flange 2. Stud Bolt 3. Gasket 4. Other flange |